What is Ectopic Pregnancy?
Ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, typically in the fallopian tubes or, rarely, in other places like the cervix or abdomen. It poses significant risks if untreated.
Causes:
- Damaged Fallopian Tubes: Scarring from past surgeries or infections.
- Hormonal Factors: Imbalances affecting egg movement.
- Birth Control: Rare pregnancies despite contraceptive use.
- Smoking: Increases risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Symptoms:
- Abdominal Pain: Severe pain on one side.
- Vaginal Bleeding: From light to heavy with pelvic pain.
- Shoulder Pain: If there's internal bleeding.
- Weakness, Dizziness, or Fainting: Due to internal bleeding.
Diagnosis:
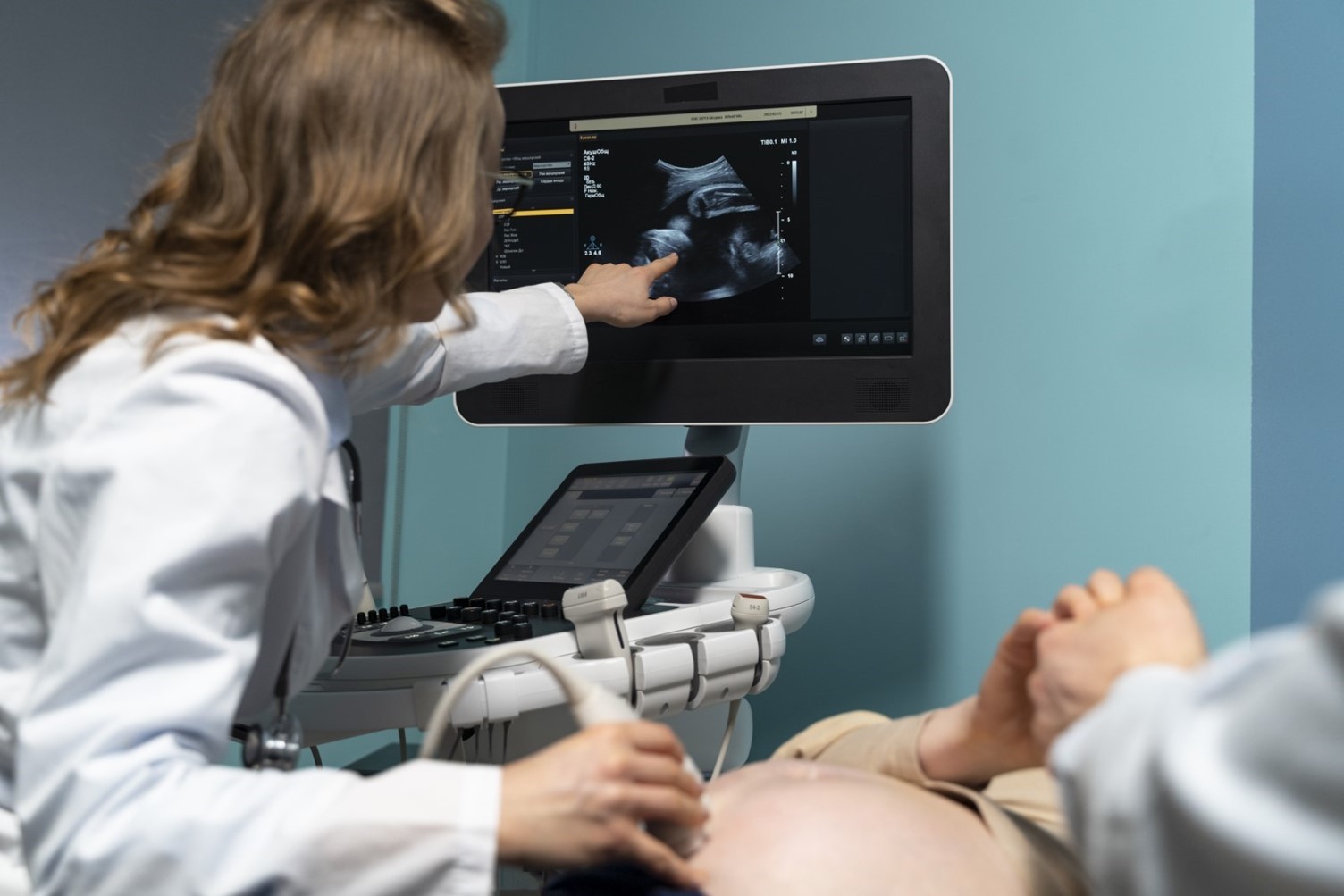
- Ultrasound: Visualizes the pregnancy's location.
- Blood Tests: Measures hCG levels.
- Pelvic Exam: Checks for tenderness or mass.
Treatment Options:
Treatment depends on the pregnancy's location and health:
- Medication: To stop cell growth if detected early.
- Surgery: Laparoscopic removal if the pregnancy is unstable.
- Expectant Management: Monitoring early stable pregnancies.
Emotional and Physical Recovery Supportive care and counselling are vital for emotional recovery and understanding future fertility.
Ectopic pregnancy requires prompt medical attention. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatments is crucial for timely intervention and health protection. Seek immediate medical help if you suspect ectopic pregnancy symptoms for proper management and improved outcomes.